 Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix, a finger-shaped pouch that projects from your colon on the lower right side of your abdomen. The appendix does not seem to have a specific purpose.
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix, a finger-shaped pouch that projects from your colon on the lower right side of your abdomen. The appendix does not seem to have a specific purpose.
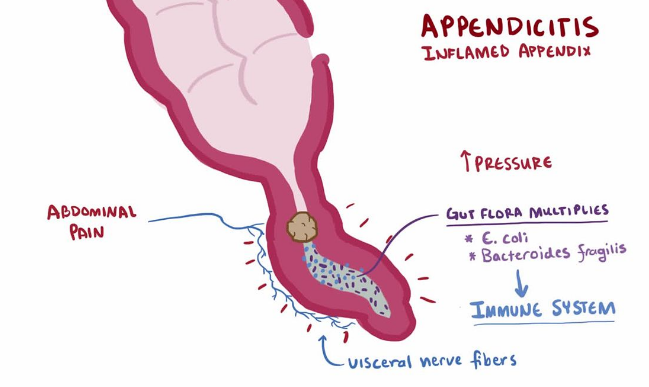
Appendicitis causes pain in your lower right abdomen. However, in most people, pain begins around the navel and then moves. As inflammation worsens, appendicitis pain typically increases and eventually becomes severe.
Although anyone can develop appendicitis, most often it occurs in people between the ages of 10 and 30. Standard treatment is surgical removal of the appendix.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of appendicitis may include:
Sudden pain that begins on the right side of the lower abdomen
Sudden pain that begins around your navel and often shifts to your lower right abdomen
Pain that worsens if you cough, walk or make other jarring movements
Nausea and vomiting
Loss of appetite
Low-grade fever that may worsen as the illness progresses
Constipation or diarrhea
Abdominal bloating
The site of your pain may vary, depending on your age and the position of your appendix. When you are pregnant, the pain may seem to come from your upper abdomen because your appendix is higher during pregnancy.
How Is Appendicitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing appendicitis can be tricky. Symptoms of appendicitis are frequently vague or extremely similar to other ailments, including gallbladder problems, bladder or urinary tract infection, Crohns disease, gastritis, intestinal infection, and ovary problems.
The following tests are usually used to help make the diagnosis:
Abdominal exam to detect inflammation
Urine test to rule out a urinary tract infection
Rectal exam
Blood test to see if your body is fighting infection
CT scans and/or ultrasound
How Is Appendicitis Treated?
Surgery to remove the appendix, which is called an appendectomy, is the standard treatment for almost all cases of appendicitis.
Generally, if appendicitis is suspected, doctors tend to err on the side of safety and quickly remove the appendix to avoid its rupture. If the appendix has formed an abscess, you may have two procedures: one to drain the abscess of pus and fluid, and a later one to remove the appendix. However, there is some research showing that treatment of acute appendicitis with antibiotics may eliminate the need for surgery in certain cases.